Test & Autopsy Results
While pharmaceutical representatives insist there is "no evidence" that gadolinium contrast agents cause harm, patients have compiled substantial documentation to the contrary. For decades, they have been willing to share their stories publicly, yet many find themselves shut out of traditional avenues for reporting their experiences.
Patients who attempted to report gadolinium-induced fibrosis, for example, discovered that the NSF database—once a key resource for recording such cases—has been closed, accompanied by claims that fibrosis no longer exists. These actions directly stifle patient experiences, which reveal ongoing harm despite the industry's marketing. Patients have turned to the internet to share data, organize evidence, and challenge the narrative.
Gadolinium metallosis - retained & stuck in a patient’s brain
Gadolinium found in organs upon autopsy
-

Liver
-

Dentate Nucleus
-

Heart
-

Bone
-

Spleen
-

Kidney
Patient gadolinium tests
-

Gadolinium in the nails
-

Gadolinium in the urine 9 days after exposure, one MRI
Patients are told that gadolinium is fully excreted from their bodies in 24-48 hours, which is a misconception, and reason for underrecognition
-

Pre-provocation Gadolinium Urine Test (same patient as next test)
-

Post-provocation chelation Gadolinium Urine Test (same patient as previous test)
-

Blood, urine, hair, and nails test from UNM. Gadolinium detected in all
In utero & breastmilk gadolinium exposure in children
-
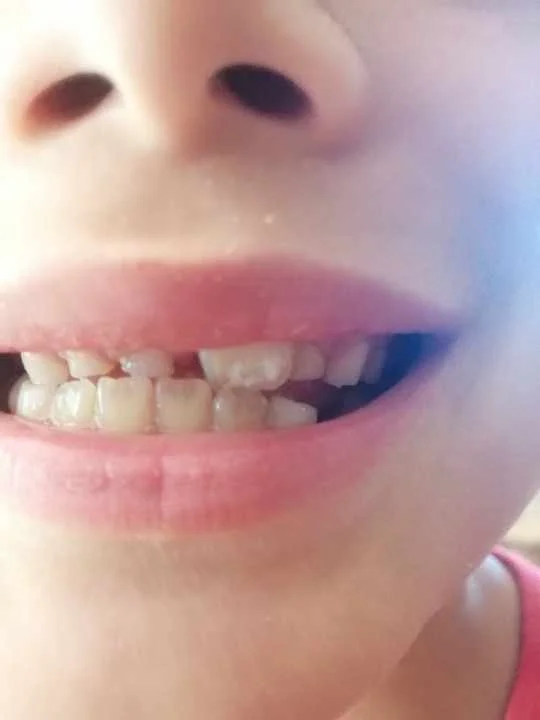
Translucent adult teeth in child exposed to gadolinium via breastmilk
This child was breastfed for three years. The first two years of life, he/she had no dental problems. However, their mother received an MRI in their third year of breastfeeding without the knowledge that she had received gadolinium or that it would pass to her baby. After her MRI, while continuing breastfeeding, her child’s baby teeth began breaking. Once she became aware of gadolinium, she tested both her breastmilk and her child for gadolinium. Both tests came back positive. When this child grew up, their adult teeth grew in with a deficiency in calcium, corroborated by their dentist. This child also experiences tooth pain and sensitivity as a result of this.
-

Breastmilk tested positive for gadolinium
-
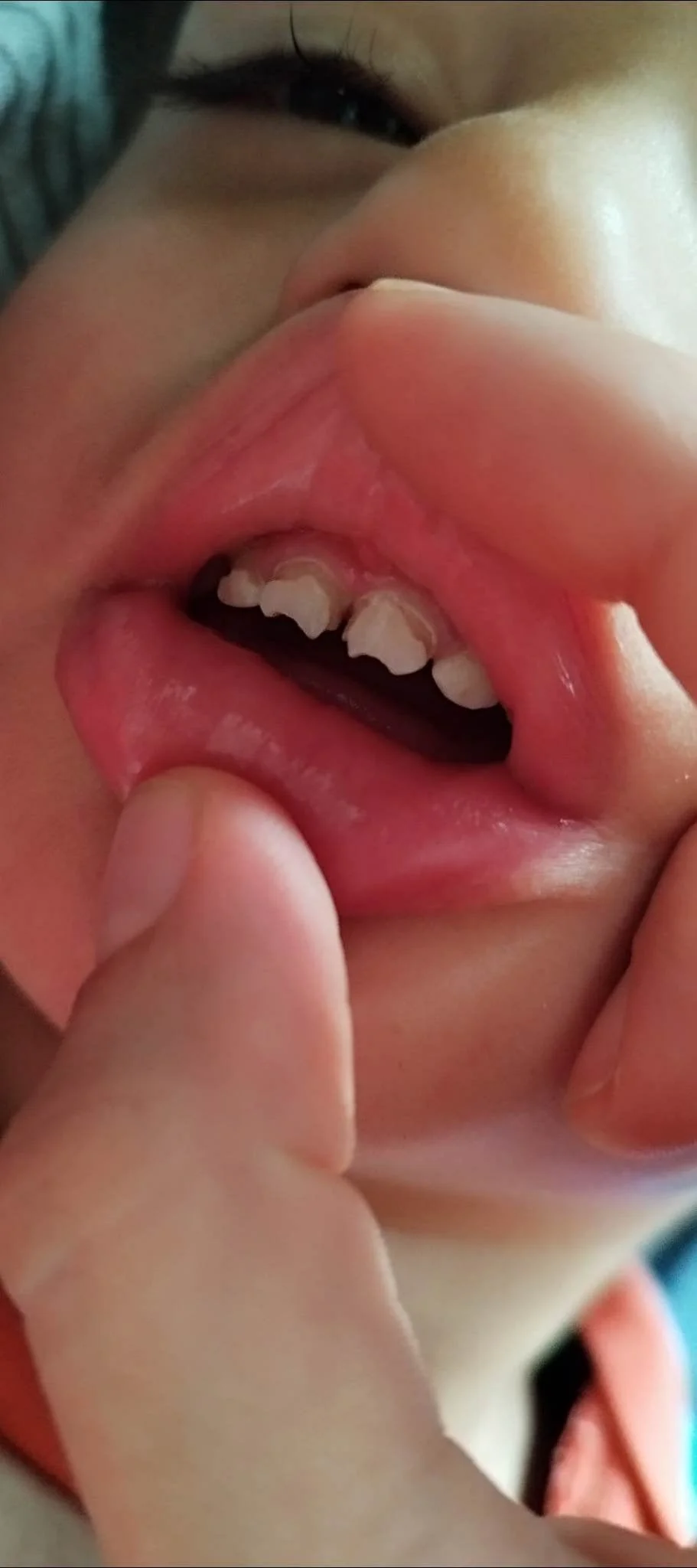
Baby teeth that grew in decalcified due to gadolinium
This baby was conceived within the first year after the mother’s exposure to gadolinium. The baby’s teeth grew in abnormally, as shown, and eventually broke off, as seen in the following photo. The condition of the child’s adult teeth is still unknown, but if they are also decalcified, the child may face lifelong consequences from the mother’s single GBCA injection.
-
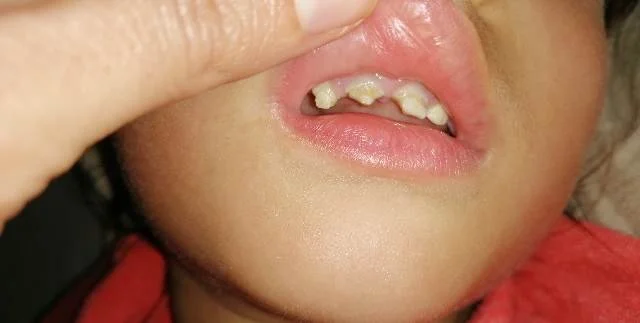
Same child as previous photo, after teeth snapped off
-

Parent reports autoimmune disease in child who breastfed during gadolinium injections
-

Another parent reports the same exact autoimmune condition in their young, gadolinium breastmilk-fed child
To see the industry deny the risks of in-utero gadolinium transfer, click here
Adult tooth decalcification after GBCA injection
-

Decalcified front teeth
This adult was in their 20s when they received two MRIs with gadolinium contrast dye. Prior to their MRIs, they had experienced 1-2 cavities in their life. Since their last MRI, their teeth have displayed rapid, significant decalcification. This individual has heavy metal tests to back up the rapid loss of calcium after their MRI.
-

Decalcification shown on heavy metals test
The chemical structure of GBCAs consists of two components: a gadolinium atom and a chelating ligand. Gadolinium mimics calcium in the body, targeting calcium-rich sites in the bloodstream and displacing it. This displacement knocks calcium free from its natural locations. Additionally, the chelating agents in GBCAs strip essential minerals from bones and other tissues. Together, these processes trigger significant calcium and mineral loss, as shown in the essential mineral test above. The graph highlights a calcium level of 385, indicating an exceptionally high excretion of calcium, which directly correlates with the visible loss of calcium from this individual’s teeth.
-

More decalcification.
There are multiple gadolinium patients who experience decalcification in this exact same spot in the teeth.
-

Cavitation that did not exist previously.
Patients also report that their teeth are more translucent, whereas before gadolinium they were opaque.
Adult tooth loss after GBCA injections
-

Tooth loss after 3 GBCAs
This individual lost their teeth after three GBCA injections.




